Our PLM Offerings
Education & Awareness
PLM Workshops
PLM Certification
Strategy & Selection
PLM Capability and Maturity Assessment
PLM Business Case/ROI Analysis
PLM RFP Creation & Review
PLM Vendor Proposal/RFP Response Analysis
PLM System Evaluation & Selection
Implementation
Business Process Design & Optimization
Rapid Results Implementation
Application Integration
Data Migration
Project Management & Recovery
Organizational Change Management
What is PLM?
Product lifecycle management or PLM is an all-encompassing approach for innovation, new product development and introduction (NPDI), and product information management from ideation to end of life. PLM systems as enabling technology for PLM integrate people, data, processes, and business systems and provide a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprise.
Business Drivers
Innovation and new product development are essential for most companies to sustain future revenue growth. Customers demand more new products in shorter time intervals, often customized to their own needs. They want more attractive designs, better performance, better quality, lower prices, and instant availability. To meet these needs companies have to be able to collaborate closely within their own organization and with partners and suppliers located in various parts of the world. At the same time companies have to manage increasing product and manufacturing complexities due to a quickly growing number of environmental and regulatory rules and requirements.
The Problem
Accelerating innovation and increasing the number of successful new product introductions is a huge challenge for most organizations today because of their traditionally serial, fragmented, manual, and paper based processes. The result is that many companies suffer from NPDI practices that are slow, resource intensive, costly, inflexible, provide little visibility, and are difficult to manage and control.
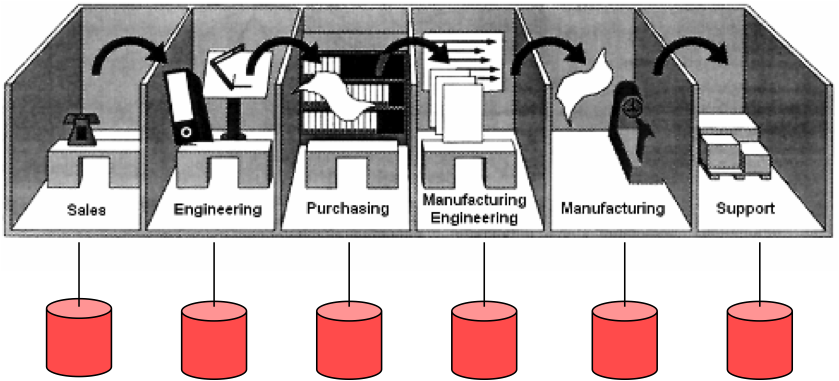
The Solution – PLM
Through its ability to integrate all product related data and processes and to eliminate boundaries in the value chain, PLM can significantly reduce non-value added activities and enable stakeholders to collaborate in real time using a consistent set of information throughout the entire product lifecycle. As a result, productivity improvements of over 60% in NPDI-related activities can been achieved through PLM-enabled, enterprise-wide data and process optimization and integration, which have allowed companies to:
- Drive innovation
- Accelerate Revenues
- Increase Productivity
- Reduce Costs
- Improve Quality
- Ensure Compliance
- Shorten Time-to-Market
In today’s highly competitive, fast-paced, and global business environment, well-designed and implemented PLM practices and technologies that support an organization’s strategies for innovation and growth can afford companies a real competitive advantage.
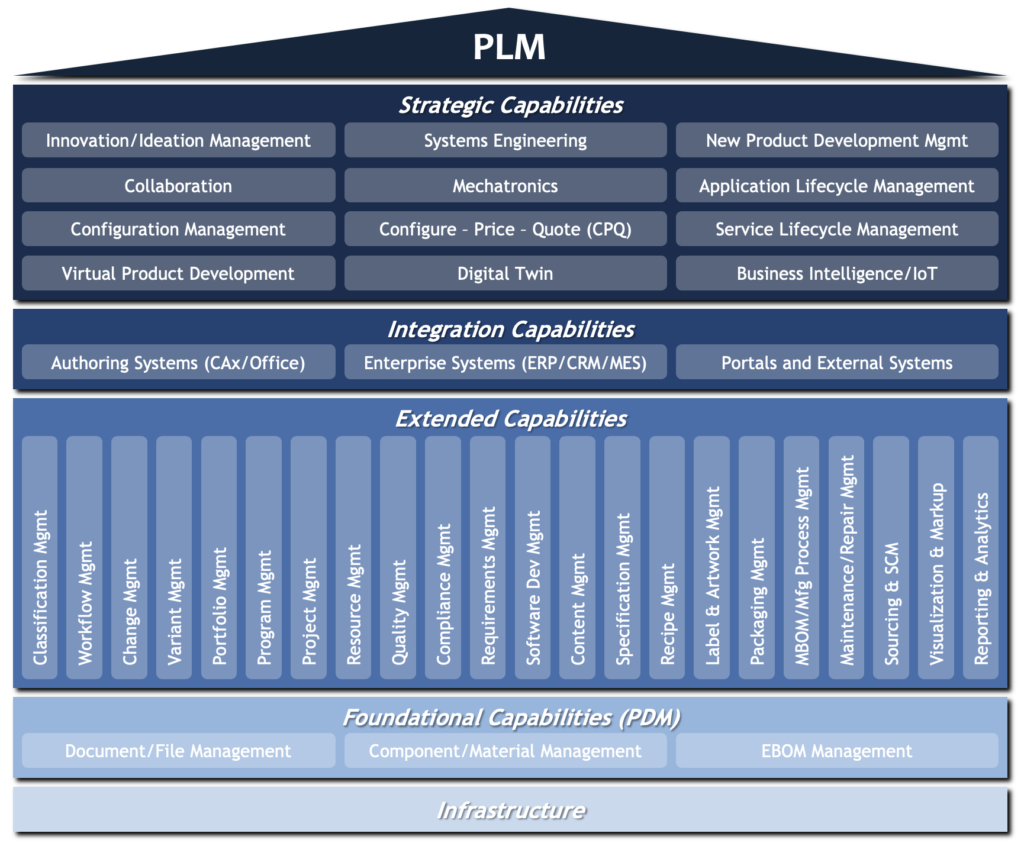
The Scope of PLM
The PLMadvisors PLM Capability Framework illustrated below includes 40 capability areas in 4 different levels – Foundational capabilities, extended capabilities, integration capabilities and strategic capabilities. The capabilities have to be implemented from the bottom up, whereby lower level capabilities are the foundation and generally a prerequisite for higher level capabilities.
The Position of PLM in the Enterprise
PLM has its highest importance and value in the beginning of the product development process, during concept, R&D, product engineering and design, manufacturing engineering, sourcing, and quality and regulatory compliance, as well as once a product has shipped for product maintenance and support. The image below illustrates the changing importance of PLM during the different phases of the product life cycle.

The Value of PLM
As stated above, PLM has many benefits. For some companies and industries the benefits are higher than for others. The higher the product or configuration complexity, ie number of requirements (customer and regulatory), components, iterations, changes and product variations, the higher the value of PLM in general.


