Quiz-summary
0 of 34 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
Information
|
You must specify a text. |
|
|
You must specify a text. |
|
|
You must specify a text. |
|
|
You must specify a text. |
|
|
You must specify an email address. |
This self-assessment allows you to determine the process and technology maturity of PLM in your organization overall and in the four areas Foundational Capabilities, Extended Capabilities, Integration Capabilities and Strategic Capabilities of the PLMadvisors PLM Framework. The result will show your absolute maturity as well as the average maturity of all respondents of this self-assessment.
Your specific answers and results are confidential and will never be shared with any third party.
For each question please select the option (A, B, C, D or E) that most accurately describes the situation in your organization.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
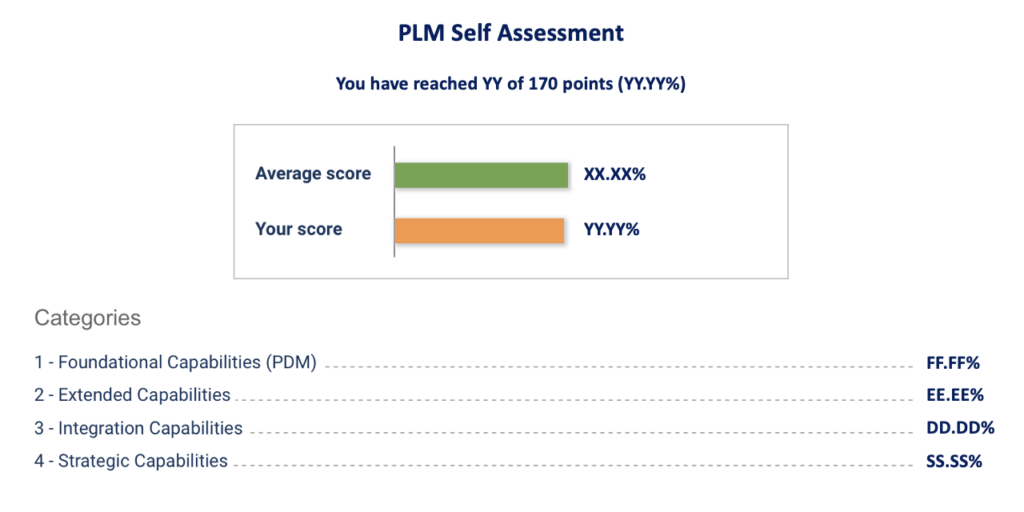
Results
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- 1 - Foundational Capabilities (PDM) 0%
- 2 - Extended Capabilities 0%
- 3 - Integration Capabilities 0%
- 4 - Strategic Capabilities 0%
-
How to interpret the result based on our PLM Maturity scale:
80 – 100%: Level 5, Integrated
60 – 80%: Level 4, Managed
40 – 60%: Level 3, Defined
20 – 40%: Level 2, Repeatable
0 – 20%: Level 1, UnstructuredFor more detailed information about your result and specific recommendations for your organization please call us at (888) 800-4PLM or send us an email to results@plmadvisors.com..
Related Information:
What is PLM?
PLM Capability & Maturity Assessment
10 Best Practices for Successful PLM Evaluations (White Paper)
PLM Insights
Upcoming Events
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 34
1. Question
Document/File Management
(A) Most documents and files are stored on local hard drives.
(B) Most documents and files are stored on shared network folders.
(C) Different documents and files are stored in separate workgroup systems (PDM, SharePoint, DMS, etc).
(D) Internal documents and files are stored and accessed in the PLM system.
(E) Internal and external documents and files are stored and accessed in the PLM system. -
Question 2 of 34
2. Question
Part/Component/Ingredient Management
(A) Item master information, such as part number, name, material, etc is only maintained on drawings and documents.
(B) Item master information is entered and maintained in different spreadsheets.
(C) Item master information is entered manually and maintained in various separate workgroup systems.
(D) Item master information is entered in one or a few enterprise systems (PLM, ERP).
(E) Item master information is entered only once in one enterprise system and automatically transferred to other systems. -
Question 3 of 34
3. Question
BOM Management
(A) BOMs are defined and managed only as text information on drawings or separate documents.
(B) BOMs are automatically created from CAD assemblies, displayed on CAD drawings and exported to Excel.
(C) BOMs are created and managed in a PDM system and manually entered into an ERP system.
(D) BOMs are automatically synchronized between CAD and PLM systems and transferred to the ERP system.
(E) BOMs are automatically and bidirectionally synchronized between the CAD, PLM and ERP systems. -
Question 4 of 34
4. Question
Configuration Management
(A) No conventions or rules for product configurations are defined.
(B) Basic rules and standards are defined and generally followed for BOM structures.
(C) Product configurations are standardized across different product lines.
(D) One or a few platforms as well as variants, options and alternate parts or configurations are defined and used.
(E) Platforms are defined and used as a basis for all products across the extended enterprise. -
Question 5 of 34
5. Question
Classification Management
(A) No part and/or document categories are defined.
(B) Basic part and document categories are defined and can be used for searching.
(C) A detailed classification hierarchy is defined and used for all parts, documents and products.
(D) Detailed attributes are defined for each category to enable search and reuse of parts, documents and products.
(E) All internal and external parties have access to and actively use the classification system. -
Question 6 of 34
6. Question
Workflow Management
(A) No processes and tasks are defined and followed.
(B) Basic tasks and work instructions are defined and generally followed by individuals.
(C) Basic processes are defined on the step and task levels and generally followed in individual departments.
(D) Processes are defined in detail on the step and task levels and followed enterprise-wide.
(E) Processes are defined in detail on the step and task levels and followed by internal and external parties. -
Question 7 of 34
7. Question
Change Management
(A) No revisioning rules and/or conventions are defined.
(B) Basic revisioning rules and conventions are defined and followed.
(C) A basic 1-stage engineering change process is defined, documented and followed.
(D) An enterprise-wide, closed-loop 3-stage change process is defined, documented and followed.
(E) A closed-loop 3-phase change process is defined, documented and followed throughout the extended enterprise. -
Question 8 of 34
8. Question
Pipeline & Portfolio Management
(A) No conventions or rules for pipeline & portfolio management are defined.
(B) Basic rules and standards are defined and generally followed for the creation and management of product/project portfolios.
(C) Current and proposed products/projects are analyzed and managed as a portfolio on a department level.
(D) Current and proposed products/projects are analyzed and managed as a portfolio on a enterprise level.
(E) Current and proposed products/projects are analyzed and managed as a portfolio on a extended enterprise level. -
Question 9 of 34
9. Question
Program Management
(A) No conventions or rules for program management are defined.
(B) Basic rules and standards are defined and generally followed for the management of programs.
(C) A program management office is established and program managers use stand-alone tools to manage programs.
(D) Internal programs are managed by corporate program management office using a PLM system.
(E) Internal and external programs are managed by a corporate program management office using a PLM system. -
Question 10 of 34
10. Question
Project Management
(A) No conventions or rules for project management are defined.
(B) Project tasks and schedules are managed manually, in Excel or in MS Project by individual project managers.
(C) Project managers use dedicated project management tools, such as MS Project Server to manage projects.
(D) Project managers use dedicated project management functionality within a PLM system to manage internal projects.
(E) PMs use dedicated project management functionality within a PLM system to manage internal and external projects. -
Question 11 of 34
11. Question
Resource Management
(A) No conventions or rules for resource management are defined.
(B) Resources are managed manually, in Excel spreadsheets or in MS Project by individual project managers.
(C) Project managers use dedicated resource management tools, such as MS Project Server to manage project resources.
(D) Project managers use dedicated resource management functionality within a PLM system to manage internal resources.
(E) PMs use dedicated resource management functionality within a PLM system to manage internal and external resources. -
Question 12 of 34
12. Question
Quality Management
(A) No quality standards are defined or followed.
(B) Basic quality standards and test procedures/results are defined and documented in Word or Excel files.
(C) Detailed quality standards and test procedures are documented, and test results captured in a quality management system.
(D) All internal quality standards, test procedures, results and data are managed in the PLM system.
(E) All internal and external quality standards, test procedures, results and data are managed in the PLM system. -
Question 13 of 34
13. Question
Compliance Management
(A) No practices and procedures are in place to ensure compliance with regulatory rules and standards.
(B) Basic procedures are defined and generally followed to ensure compliance with the most important regulatory rules.
(C) Detailed procedures are defined and documented and a dedicated compliance management system is used.
(D) The PLM system enables employees to keep track of all rules and regulations and ensures and documents compliance.
(E) The PLM system is automatically updated with new regulatory rules and ensures and documents compliance. -
Question 14 of 34
14. Question
Requirements Management
(A) No practices and procedures are in place to capture and manage requirements.
(B) Basic practices and procedures are defined and generally followed to capture and track requirements in Word or Excel.
(C) Requirements are systematically defined, documented and tracked using a dedicated requirements management system.
(D) Internal requirements are defined, documented, managed and associated with relevant product data in PLM.
(E) Internal and external requirements are defined, documented, managed and associated with product data in PLM. -
Question 15 of 34
15. Question
Source Code Management
(A) No practices and procedures are in place to manage software source code.
(B) Source code is stored on network folders during development and after release.
(C) Source code is managed in a dedicated source code management system during development and after release.
(D) Source code is managed in the PLM system and executables are part of the product BOM.
(E) Source code is managed in the PLM system and internal and external executables are part of the product BOM. -
Question 16 of 34
16. Question
Content Management
(A) No practices and procedures are in place to manage content in documents as objects.
(B) Basic practices and procedures are in place to use and reuse content objects in multiple documents.
(C) A library of content objects is available in a content mgmt system and used in most documents.
(D) A library of content objects is defined and managed in the PLM system and used in internal documents.
(E) A library of content objects is defined and managed in the PLM system and used by internal and external parties. -
Question 17 of 34
17. Question
Formula & Recipe Management
(A) No practices and procedures are in place to manage formulas and recipes.
(B) Formulas and recipes are created in Word or Excel and stored on shared network folders.
(C) A dedicated formula and recipe management system is used to create and maintain all formulas and recipes.
(D) All formulas and recipes are created and managed by internal parties in the PLM system.
(E) All formulas and recipes are created and managed by internal and external parties in the PLM system. -
Question 18 of 34
18. Question
Manufacturing Process Management
(A) No practices and procedures in place to manage manufacturing processes.
(B) Basic manufacturing processes and procedures are defined and documented in Word or Excel.
(C) A dedicated manufacturing process management system is used to create and manage all manufacturing processes.
(D) Detailed practices and procedures are in place to create and manage manufacturing processes in the PLM system.
(E) Detailed practices and procedures are in place to manage internal and external manufacturing processes in the PLM system. -
Question 19 of 34
19. Question
Maintenance & Repair Operations (MRO) Management
(A) No practices and procedures in place for MRO management.
(B) Basic MRO practices and procedures are documented in Word or Excel and stored on shared network drives.
(C) Detailed MRO practices and procedures are defined and managed in a dedicated MRO system.
(D) Detailed MRO procedures are managed in the PLM system and associated with the respective product data.
(E) Detailed MRO procedures and information are managed in the PLM system and reflect the actual maintenance status. -
Question 20 of 34
20. Question
Sourcing and Supply Chain Management (SCM)
(A) No practices, procedures or tools are in place for sourcing and supply chain management.
(B) Supplier information is managed by procurement staff in Word or Excel files, Outlook or personal databases.
(C) A supply chain management tool is used by procurement staff to manage supplier information.
(D) Vendor and purchasing data is managed in the PLM system and associated with the respective parts.
(E) Vendor and purchasing data is managed in the PLM system. Changes are automatically communicated with vendors. -
Question 21 of 34
21. Question
Visualization and Markup
(A) No practices, procedures or tools are in place for visualization and markup.
(B) Documents are viewed and marked up in a basic tool, shared via email and stored on network drives.
(C) Documents are viewed and marked up in a visualization and markup tool that is part of a PDM system.
(D) Documents are viewed and marked up in an integrated visualization and markup module in the PLM system.
(E) Documents are viewed and marked up by all internal and external parties in the PLM system. -
Question 22 of 34
22. Question
Reporting and Analytics
(A) No reports are available. All information has to be gathered on an ad-hoc basis.
(B) Individual workplace tools are set up to provide basic information on an as-needed basis.
(C) Detailed department-level reports are available in workgroup tools.
(D) Detailed enterprise-level reports are available in the PLM system to internal parties.
(E) Detailed enterprise-level reports are available in the PLM system to internal and external parties. -
Question 23 of 34
23. Question
Authoring Systems (CAx, Office)
(A) No integrations are available. All data is entered manually in the different tools.
(B) No integrations are available. Data is manually exported and imported using text, CSV or Excel files.
(C) Data is transferred using integrations between authoring tools (CAx, Office) and different workgroup management tools.
(D) Data is transferred using integrations between authoring tools (CAx, Office) and a PLM system.
(E) Data is bidirectionally synchronized between authoring tools (CAx, Office) and a PLM system. -
Question 24 of 34
24. Question
Enterprise Systems (ERP, MES, CRM)
(A) No integrations are available. All data is entered manually in the different tools.
(B) No integrations are available. Data is manually exported and imported using text, CSV or Excel files.
(C) Data is transferred using integrations between workgroup data management tools and enterprise systems.
(D) Data is transferred using integrations between the PLM system and other enterprise systems.
(E) Data is bidirectionally synchronized between the PLM system and other enterprise systems. -
Question 25 of 34
25. Question
Portals and External Systems
(A) No integrations are available. All data is entered or uploaded manually in the different systems.
(B) No integrations are available. Data is manually exported and imported using text, CSV or Excel files.
(C) Documents and data are automatically uploaded to portals and external systems upon user request.
(D) Documents and data are automatically uploaded from the PLM system to portals and external systems.
(E) Documents and data are automatically synchronized between the PLM system and portals and external systems. -
Question 26 of 34
26. Question
Innovation/Ideation
(A) No practices and procedures are in place to manage the creation, capture and use of ideas.
(B) Basic practices are in place to manage the creation, capture and use of ideas using Excel, Word or similar tools.
(C) Detailed practices are in place to manage the creation, capture and use of ideas using workgroup tools (Access, Lotus Notes).
(D) Detailed practices are in place to manage the methodical creation, capture and use of ideas with the PLM system.
(E) Detailed practices are in place to manage the methodical creation, capture and use of internal and external ideas with PLM. -
Question 27 of 34
27. Question
Systems Engineering
(A) No practices and procedures are in place for systems engineering.
(B) Basic practices and procedures are in place and are generally followed for systems engineering.
(C) Requirements are managed for entire systems (HW, EE, SW) through the life of the product in a dedicated tool.
(D) Requirements are managed for entire systems through the life of the product and associated to product data in PLM.
(E) Internal and external requirements are managed for entire systems through the life of the product in PLM. -
Question 28 of 34
28. Question
New Product Development (NPD) Management
(A) No practices and procedures are in place for new product development (NPD).
(B) A basic NPD process is in place and is generally followed.
(C) A NPD process is defined, including deliverables, roles and responsibilities and enabled by a workflow mgmt system.
(D) A detailed NPD stage gate process is defined and enabled by a PLM system.
(E) A NPD stage gate process that includes all internal and external parties is defined and enabled by a PLM system. -
Question 29 of 34
29. Question
Virtual Product Development (VPD)
(A) No practices and procedures are in place for virtual product development (VPD).
(B) Products are modeled and assembled in CAD, analyzed using CAE and manufactured using CAM.
(C) Products are modeled, analyzed and manufactured in CAx systems and managed in different workgroup solutions.
(D) Products are modeled, analyzed and manufactured in CAx systems and managed associatively in PLM.
(E) Internal and supplier products are modeled, analyzed and manufactured in CAx systems and managed in PLM. -
Question 30 of 34
30. Question
Mechatronics
(A) No practices and procedures are in place for mechatronics.
(B) Basic practices are in place for the integrated development of products consisting of HW, EE and SW components.
(C) Different workgroup solutions (PDM, source code mgmt, etc) are used to manage the data and processes of each area.
(D) All mechanical, electric, electronic and software data and processes are managed in a central PLM system.
(E) All internal and vendor mechanical, electric, electronic and software data and processes are managed in PLM. -
Question 31 of 34
31. Question
Collaboration
(A) No practices and processes are in place for collaboration.
(B) Collaboration and file exchange is done using email and other individual tools (Skype, etc)
(C) SharePoint, dedicated collaboration tools or other workgroup solutions are used for collaboration and file exchange.
(D) The PLM system is used for collaboration and internal information sharing.
(E) The PLM system is used for collaboration and internal and external information sharing. -
Question 32 of 34
32. Question
Custom Product Configuration (CPQ)
(A) No practices, processes and tools are in place for custom product configuration.
(B) Products are configured to customer specific needs in CAD and Excel speadsheets.
(C) Custom products are configured using a sales configurator, a PDM system and an ERP system.
(D) Products are configured in a sales configurator, which is populated from PLM and then feeds into ERP.
(E) All configuration rules are managed in a central rules engine and repository, which is integrated with the sales configurator, the PLM system and the ERP system and ensures that only technically possible and commercially available options can be selected. -
Question 33 of 34
33. Question
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM)
(A) No practices, processes and tools are in place for application lifecycle management.
(B) Software is developed using standalone source code management systems.
(C) The company uses a dedicated ALM system to support software development.
(D) The company uses PLM to enable the integrated development of hardware and software.
(E) The company uses PLM to collaborate closely with external partners in the integrated development of HW and SW. -
Question 34 of 34
34. Question
Business Intelligence (BI)
(A) Required data is gathered manually on an ad-hoc basis.
(B) Data is compiled in individual tools such as Excel or Access databases and made available as needed.
(C) Information is analyzed and presented using reporting tools, such as MS Reporting Services, Cognos, etc.
(D) Internal information is analyzed and presented using reporting functionality integrated in the PLM system.
(E) Internal and external information is analyzed and presented using reporting functionality integrated in PLM.